Types of Risk Assessment Methodologies
Assessing the level of cyber risk in a business system entails discovering the types of cyber-attacks
.png) Technology accompanied by digitization has permeated many business disciplines, dominating many industries like financial services, medical records, manufacturing processes, and even military activities and equipment. Therefore, cyber security has become integral to running private and public businesses and service entities of various forms in the 21st century.
Technology accompanied by digitization has permeated many business disciplines, dominating many industries like financial services, medical records, manufacturing processes, and even military activities and equipment. Therefore, cyber security has become integral to running private and public businesses and service entities of various forms in the 21st century.
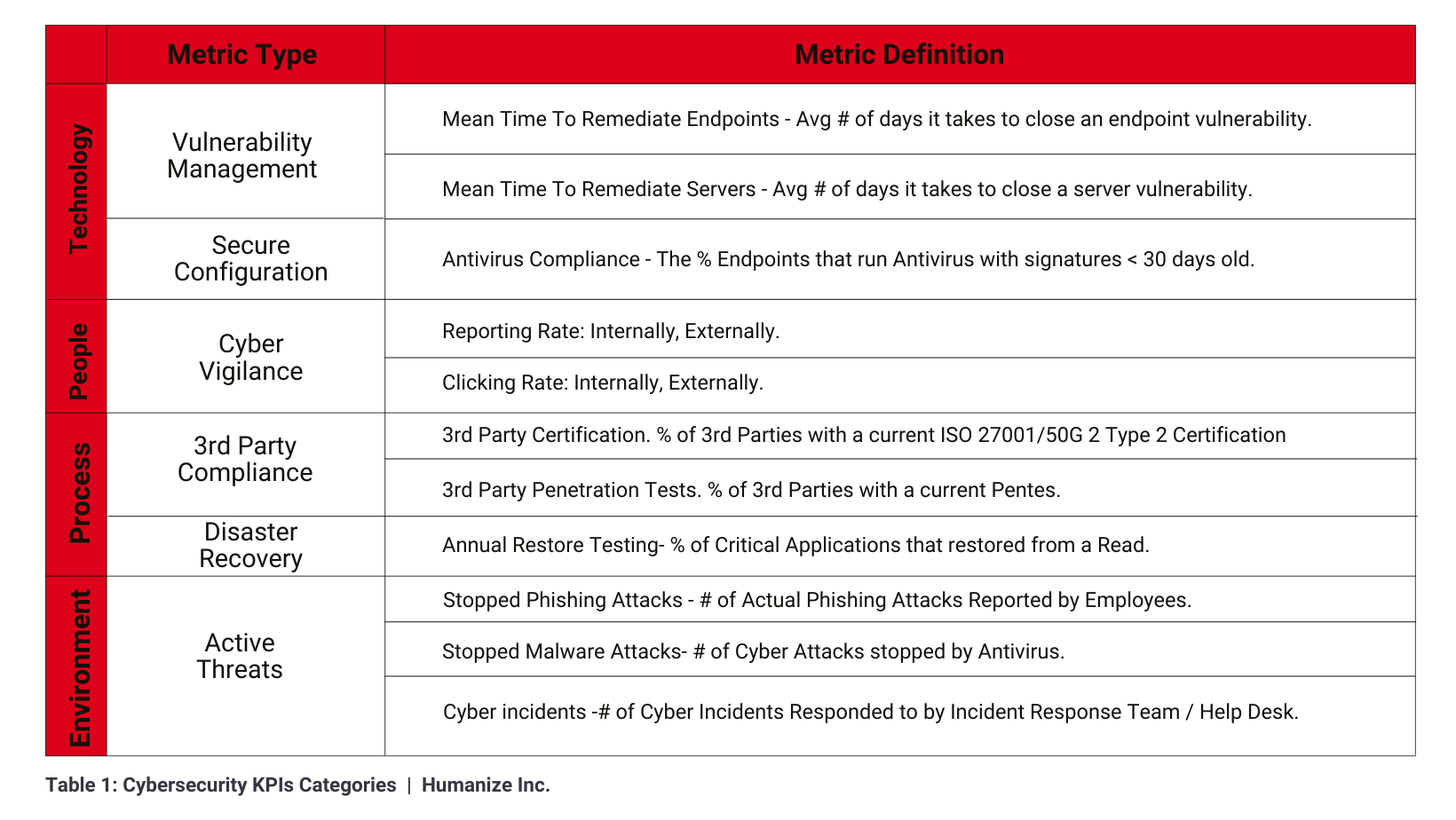 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability ManagementVulnerability is a flaw or a weakness such as a bug or inadequately secured firewall that cyber criminals can use to access devices. Cyberattack vulnerabilities on endpoints, workstations, and systems are discovered, ranked, assessed, treated, and reported via vulnerability management.
Spotting, prioritizing, and putting software problems in context increase cyber security, especially since new security flaws appear as networks and operating systems evolve. However, vulnerability management includes primary metrics such as:
The time it takes for a security flaw to be exploited before it is discovered. It's best if that time frame is as short as possible.
The average time it takes to address the vulnerability and alleviate the attack.
The number of patches deployed and the time required to apply certain patches.
A list of unresolved high-risk vulnerabilities for which no fix has been identified to avert future dangers.
A measure of the resolution method's effectiveness; a high rate indicates the patched repair process was defective.
Keeping track of the resolved vulnerabilities helps assess the effectiveness of the remediation process.

Secure configurations are the measures adopted to reduce cyber threats. Hardware and software manufacturers usually provide them with default settings, making them easier to breach by cybercriminals. Therefore, improving the company's cyber security requires a properly configured secure environment. Antivirus software is one of the fundamental measures to monitor the system for virus intrusions. And the most important step is ensuring the antivirus software is up-to-date and compatible with the system.
Center for Internet Security (CIS) benchmarks are another crucial metric since they encompass everything from initial setup to configuration of all aspects of the IT system, guaranteeing the company's cyber security compliance with industry-agreed cybersecurity standards.
Individuals are the most vulnerable part of any cyber defense system because of their propensity for making mistakes and because they are vulnerable to the most damaging type of cybersecurity threat: social engineering, particularly phishing. As a result, it is essential to maintain a high degree of cyber alertness within the workforce to lessen the cyber danger.
Phishing exercises and internal and external reports are used in the Cyber Vigilance KPI to illustrate how well-equipped personnel deal with such a threat; it includes two main metrics:
1. Internally: This metric shows the percentage of employees who failed the test and clicked the phishing link
2. Externally: Reports how much people respond to phishing tests across the industry
The lower the rate, the better.
1. Internally: This metric shows the percentage of employees who reported the phishing test to the IT team or help desk
2. Externally: Reports on the percentage of people responding to phishing tests across the industry
The higher the rate, the better.
More and more businesses rely on external services like patch management software and online payment processing. In doing so, they expose themselves to potential cyber-attacks by disclosing private information to untrusted third parties. Therefore, there are indicators to evaluate while collaborating with other parties:
CAIQ provides a recorded preference of what controls exist in cloud services and aids in determining if the 3rd Party is appropriately secure.
When a third party is said to be ISO 27001 compliant, it signifies that their information security management systems have been audited by authoritative certification bodies and found to be in accordance with the standard.
The purpose of a penetration test, also known as a pen test, is to expose the security flaws in an organization. 3rd Parties with a recently conducted high-quality pen test are preferable to deal with.
Disaster recovery KPI reveals how well the IT recovery teams will reclaim control after a cyber-attack. Usually, cybersecurity professionals put together a recovery plan that includes a disaster team, backups, impact assessment, and ensures business continuity. Therefore, tests must be conducted to have metrics for evaluating the disaster plan.
An approach that verifies if a system can allocate additional resources and back up all data and actions in the event of an unexpected failure. The test's outcome indicates the system's resilience in the face of unforeseen disruptions and the capacity to accommodate more servers.
Incomplete data backups, faulty backup software, or an upgrade that breaks the backup system are just a few of the many potential causes of a backup system failing to work as intended. Therefore, verifying the process of restoring backups during a disaster drill will reveal which backups are being restored correctly and which are damaged, allowing for the necessary fixes to be made before an actual emergency occurs.
One of the key performance indicators (KPIs) for cyber security is the number of genuine cyber security threats that have been addressed.
The included metrics:
Overall effective cyber security precautions get better with higher ratings.
Maintaining a high standard of cyber security is time-consuming yet essential—key performance indicators (KPIs) for cyber security aid IT departments in monitoring and enhancing their efforts. While certain KPIs are technology-related, the human element must also be addressed. Thus, to safeguard your business, monitor the aforementioned cyber security KPIs.
Monitoring cybersecurity KPIs is a difficult and time-consuming task that requires engaging cyber security professionals. However, administrative managers can also participate in the process by utilizing dedicated software that tracks the status and generates reports in real-time. Still, most reports are usually complicated and can't be interpreted easily.